Post It On KidzTalk Homework Help
Report a search problem
mobile version
Copyright 2005-2024 KidzSearch.com

|
| Archaea (Archaebacteria) | |
|---|---|
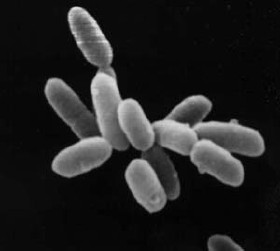 | |
| Halobacterium sp. strain NRC-1, each cell about 5 μm long | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Unrecognized taxon (fix): | Archaea |
| Kingdoms and phyla | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The Archaea (or Archea) are a group of single-celled organisms. The name comes from Greek αρχαία, "old ones". They are a major division of living organisms.
Archaea are tiny, simple organisms. They were originally discovered in extreme environments (extremophiles), but are now thought to be common to more average conditions. Many can survive at very high (over 80 °C) or very low temperatures, or highly salty, acidic or alkaline water. Some have been found in geysers, black smokers, oil wells, and hot vents in the deep ocean. Recent research has found ammonia-eating archaea in soil and seawater.
In the past they had been classed with bacteria as prokaryotes (or Kingdom Monera) and named archaebacteria, but this is a mistake. The Archaea have an independent evolutionary history and show many differences in their biochemistry from other forms of life. They are now classified as a separate domain in the three-domain system. In this system, the three distinct branches of evolutionary descent are the Archaea, Bacteria and Eukaryota.
